General warehouse quotation will comprise several parts, mainly warehouse operating cost, storage cost, logistics cost, and value-added service fee.
Warehouse operation expense generally includes warehouse inbound and warehouse outbound. Simply put, it is the expense generated by the warehouse to help customers complete the necessary operations of supply chain circulation.
The storage charge is the opposite of the warehouse operation charge, which is static. The storage charge in many warehouses also exists as a hedge against the warehouse operation charge, which can be seen from the setting of the rent-free period.
Value-added service fee is mainly charged for some possible actions, which can help customers enjoy different service levels.
Compared with other warehouse expenses, storage expenses have the following features:
The storage fee is calculated daily, regardless of the volume of the service. In the WMS system, the originating point is generally a scheduled task, and no specific document is associated.
Whether it is operation cost or logistics cost, it is an expense. Generally speaking, it can be decided whether to accept or not according to the actual requirements of the warehouse. Some processes are triggered to the point of charging. But storage fees are generally required to cover the whole warehouse. It is not possible to only collect the storage fee of the products on the pallet without collecting the storage cost of the products on the storage location, so be careful not to miss the cost when calculating the warehousing cost.
Especially for some warehouses with complex storage cost calculation methods, to calculate the storage cost of a specific day, it is necessary to restore the inventory situation of the day, and when the warehouse has no system or the system is not strong enough, it is difficult to restore the inventory scene of a very detailed day in history, so it can not be repeated. And other expenses recalculation is relatively simple as long as you get that single’s documents.
Different warehouses may charge different amounts for other businesses.

Generally appearing in the quotation used for a consignment, it is based on the inventory quantity of the product and the inbound and outbound information to calculate. The warehouse can calculate the storage fee of the day according to the records of the products in stock and the size of the products on hand. If there is a record of the goods in and out of the warehouse, it can also realize the recalculation at a specified point in time. The disadvantage is that packaging and other factors are not considered, and the cost item of warehouse space occupation cannot be completely corresponding.

Generally appearing in the warehouse business of transshipment or bulk goods, the pallet is used as the billing condition. The number of pallets can be used to quickly calculate the number of storage charges, and the billing objects involved are smaller than those calculated by volume. The disadvantage is that the warehouse’s input and output requirements are relatively high, and the pallet must be used inbound and outbound. If the pallet is removed for a small package out of the warehouse, the billing is more complicated. Often, there is no record of the removal of pallets or the delivery of goods on a pallet, so more refined inventory management and records are needed.

Some warehouses use the way to calculate the warehouse location occupation, different warehouse locations or Bin set different prices, for their customers only need to record how many Bin their goods are used, it is more convenient to count. However, the disadvantage is that if the customer’s goods flow is relatively large, the storage space the customer occupies needs to be calculated frequently. The method of renting warehouse space in advance can solve the recording problem. For example, customer A rents 100 warehouse Spaces in advance and charges according to 100 as long as he can put them down. However, the disadvantage is that this will bring unnecessary expenses to the customer.
Generally, as a supplement to volume billing, when a customer’s products are small and the number of products is not large, the warehouse will choose to use the number of products to calculate the storage fee to increase the total inventory cost and reduce the waste of space caused by the independent storage of the customer’s products (many warehouses will not mix the customer’s products, a small number of products also take up a whole warehouse). The disadvantage is that it is unreasonable if the entire warehouse is used this way. The volume of significant and small products is different, which must be addressed.
The final formula we use to calculate storage time is:
Storage charge = charging unit price * charging quantity
The unit price is affected by several factors:
As we have said, the storage fee revenue ranks low in the warehouse revenue. In addition, based on the warehouse’s utilization rate, improving inventory turnover is the direction that each warehouse pursues to enhance its revenue. So those long-term unsalable inventories must be adjusted through high storage fees because it does not bring any operating costs and freight income.
In the peak season, the actuating rate of the product is relatively high. According to the principle of the above article, additional adjustment is needed for the products with inventory costs. That is, the storage costs will be higher in the peak season.
The customer itself is also a factor affecting the storage fee. The storage fee may differ due to different agreements when acquiring customers or during operation. The warehouse will adjust the incentive measures for good customers or punishment measures for wrong customers. All these measures can be realized in the storage fee. For example, we mentioned above for customers with low moving pin rates using per piece storage charges.
We have different types of storage: product inventory (mainly for one-piece consignment), transfer, and return. Each of these three types of storage has its characteristics, which can affect how the storage is billed.
The feature of product inventory is integrated into and distributed, so the first consideration of product inventory is to find a common feature of all products to be used as the billing object: generally product volume;
The second is to deal with the problem of tail goods, that is, through the number of charges or storage location to avoid small volume products for the occupation of large space;
Thirdly, the rent-free period needs to be specified on each product, which
leads to the warehouse having to get very detailed product delivery details and know which batch of products are from the warehouse.
The transfer inventory is characterized by integral in and out, so the transferred inventory can not need specific products, only need boxes or pallets. The focus of transfer accounting is how to do simple and fast accounting, so the number of pallets is a good way of accounting.
In addition, because transshipment tends to take up more warehouse space than product inventory, some warehouses will have a shorter rent-free period for transshipment inventory.
The characteristic of returned inventory is that returns often do not know the specific product but only know which customer’s box or pallet. Moreover, sporadic return warehouses are unwilling to deal with the goods quickly but hope to wait for some time for unified processing.
Therefore, the subjective intention of producing inventory is in the warehouse, so many warehouses do not charge the return storage fee or directly charge according to whether the goods are available in the warehouse or the returned goods allocated to the customer.
In the past, customers did not dare to invest too much energy in calculating storage fees because it is challenging to figure out. The income is not so high, but with the current development trend of the industry, there are many goods in a state of delayed storage, so the calculation of storage fees is more important. The setting and analysis of storage fees are also developing in the direction of refinement. The number of accounting scenarios and modes is increasing.
Three problems need to be solved for WMS to make reasonable storage fees:
The first is that the storage fee charging needs to be flexibly adapted to various charging scenarios, no matter the storage methods, attributes of the product storage, or different customers;
The second is the comprehensiveness of storage charging, ensuring that the charging model covers the whole warehouse goods in the case of multiple charging methods;
The third is the traceability of storage costs. Storage costs can restore the calculated scenario and recalculate, which requires vital inventory records.
In order to solve the above problems, the ShipOut WMS system mainly implements the following solutions for storage fees:
1. Provide product, transfer, and return inventory, three kinds of storage charging systems so the warehouse can configure the charging scheme according to its situation.
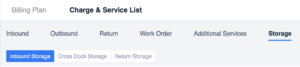
2. Provide different dimensions of storage cost calculation (MU, boxes, SKUs), conditions and formulas can be configured, and priorities can be configured in situations to ensure that various cases can be calculated and cover all goods in the warehouse.
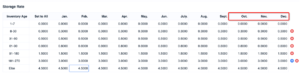
3. Billing settings support custom inventory age and off-peak tables.
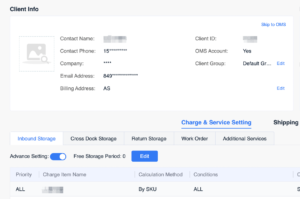
4. The storage fee pricing system can be configured independently for specific customers.
Choose a suitable and customizable warehouse management system to help you effectively solve the complex storage cost calculation problem. Contact us for a better solution.

Last updated: 2025-05-06

Last updated: 2025-04-01

Last updated: 2025-03-03
Last updated: 2025-02-05